Losses may be greater than investment value
|
|
|
|



Margin Trading

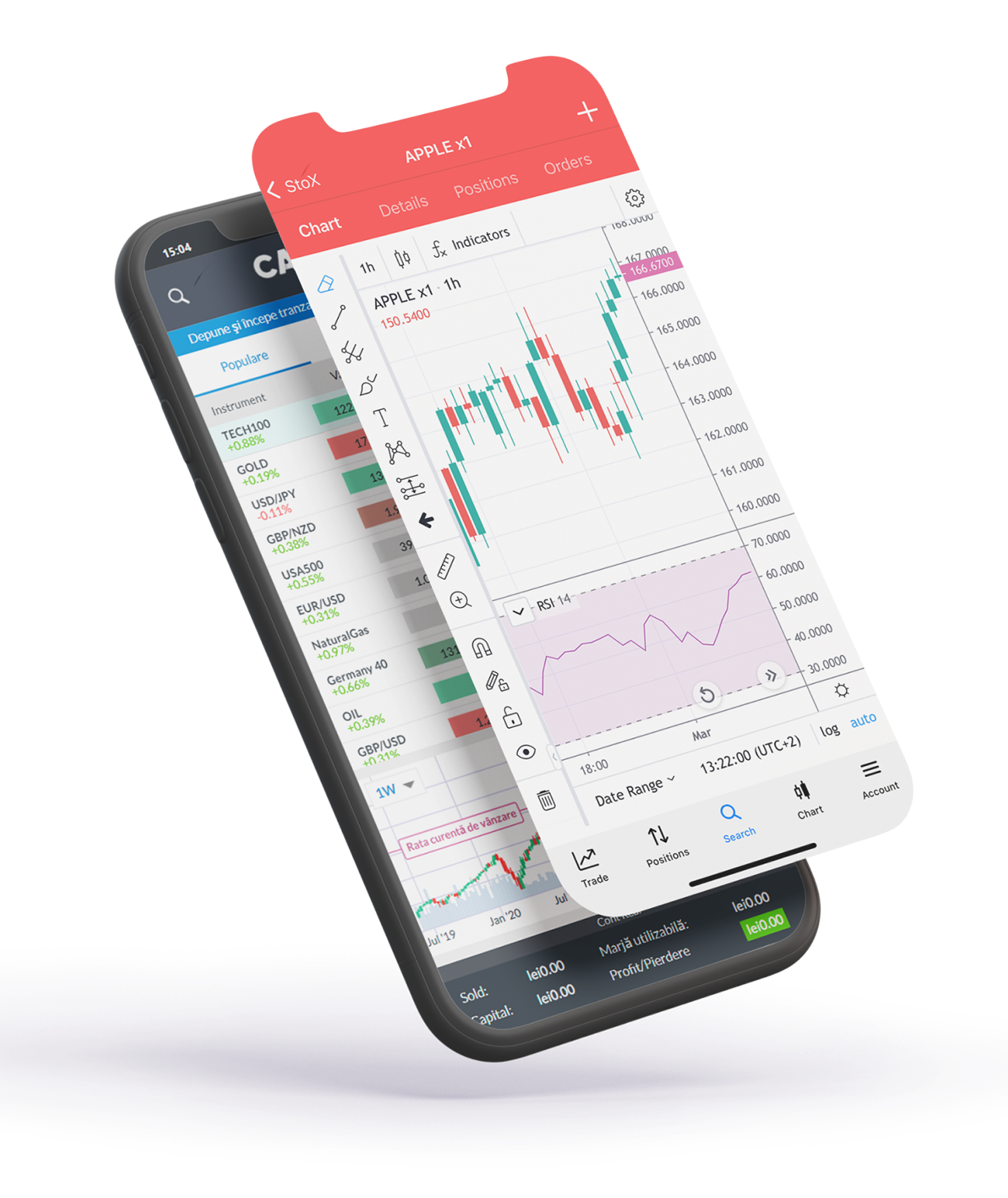
What is Margin Trading?
There are two margin definitions. Securities margin is borrowing money to buy stock. However, commodities margin involves putting in your own cash as collateral for the contract.
Margin borrowing is only for experienced investors with high risk tolerance. You may lose more than your initial investment.
Before trading on margin,
understand the following risks
-
-
Greater potential risk of loss
-
Additional costs from margin interest charges
-
Potential margin calls or liquidation of securities

Leverage Advantage
Use the cash or securities in your account as leverage to increase your trading and earning power.
Leverage Advantage
Use the cash or securities in your account as leverage to increase your trading and earning power.

Low Interest
Get the lowest interest rates. Our margin rates are among the lowest available in the industry.
Low Interest
Get the lowest interest rates. Our margin rates are among the lowest available in the industry.

Mutual Funds
Diversify trading strategies with short selling, options and futures contracts, or currency trading.
Mutual Funds
Diversify trading strategies with short selling, options and futures contracts, or currency trading.

Loan Convenience
Borrow against a margin account at any time and repay the loan on your own schedule.
Loan Convenience
Borrow against a margin account at any time and repay the loan on your own schedule.




Rules-based vs. Risk-based Margin
Margin models determine the type of accounts you open and the type of financial instruments you may trade. Trading on margin uses two key methodologies: rules-based and risk-based margin.
In rules-based margin systems, your margin obligations are calculated by a defined formula and applied to each marginable product. This is the more common type of margin strategy used by securities traders.
In risk-based margin systems, margin calculations are based on the risk inherent in your trading portfolio. The positions in your account are evaluated, including any hedged positions that decrease potential risk, and based on their risk profile, used to create your margin requirements.
